Reducing food waste – Shared Social Economic Pathways (SSPs)
June 22, 2021 2021-06-22 7:16Reducing food waste – Shared Social Economic Pathways (SSPs)

Reducing food waste – Shared Social Economic Pathways (SSPs)
Introduction
This research paper focuses on reducing food waste as it has a direct impact on environmental sustainability. The current adoption of westernized food such as foods that are high in carbohydrates; added sugars and low in fruits and vegetables have a direct impact on the population health and environmental sustainability. Food wastage arises due to people sticking to one diet and forfeiting other available food types. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) fits in the research topic as the wastage of food leads to environmental degradation ultimately impacting climate. The wasted food that is not consumed such as fruits and vegetables are producing vast amounts of pesticides, fertilizers, and irrigation mechanisms that leads to extensive environmental degradation. Therefore, the reduced food demand would lead to reduced food wastage resulting in minimal impact on climate.
Shared Social Economic Pathways (SSPs)
Riahi, K., van Vuuren, D. P., Kriegler, E., Edmonds, J., O’Neill, B. C., Fujimori, S., … Tavoni, M. (2017). The Shared Socioeconomic Pathways and their energy, land use, and greenhouse gas emissions implications: An overview. Global Environmental Change, 42, 153–168. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.05.009
SSPs describe a range of activities that are meant to mitigate the impact on climate and enable the adaptation of the climatic changes amongst different people. The first SSP addresses the effective use of land resources, reduction of food waste, reduction of income inequalities and less resource-intensive consumption of food products. The SSP1 will lead to the empowerment of poor people to afford a healthy diet; reduction in food waste will help eliminate the wastage of resources as well as the negative impact of the food waste such as increased levels of emission of CO2 gases into the environment.
SSP2 addresses the medium challenges that can be adapted in mitigation against the impacts of climate changes. The challenges are indicative of an increase in technological progress, production and consumption rates, as well as medium income. The capacity to mitigate the impact of the environmental challenges lay in the ability of the citizens to adapt to new climatic changes. Lack of proper technological advancement measures may derail the progress in achieving a higher rate of food production which will increase the price of the food supply. This will create a lack of purchasing power of a healthy diet for the general population and may cause people to resort to unhealthy diets leading to larger food wastage in the long run.
SSP3 entails high challenges to climatic adaptation and environmental change. The SSP3 comprises of a rocky part in the achievement of the set goals towards environmental sustainability. Efforts shift from worldwide to the region and country-specific changes. Countries conduct mitigation and adaptation programs at the expense of other countries. The perspective is indicative of the changes in the investment in education and technological sectors. The environmental policies formulated focuses on the local area only.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
SSP4 focuses on the inequality in society that is characterized by low mitigation efforts versus high adaptation efforts. There have been differing amounts of inequalities in investment in human capital and mitigation efforts leading to the variance in stratification both within and across countries. The fragmentation in societies leading some communities living in poor backgrounds with minimal income and labor-intensive jobs with investment in the carbon-intensive system such as coal as well as low carbon sources. There are disparities in the environmental changes that different countries or economies can implement.
SSP5 focuses on fossil-fueled development where there are high challenges to mitigation efforts as well as low challenges in adaptation efforts. The competitiveness in the global market helps in technological advancements meant to help in mitigation of the impact of the environmental challenges to the environment. The adoption of resource and energy-intensive lifestyles is meant to push for economic and social developments. SSP5 envisions the 22nd century where local and global efforts towards sustainable development are in place.
The reduction of food waste connects to SSP1. The peak in population and the changes in income levels impact the affordability of many westernized diets leading to wastage of a lot of indigenous crops, fruits and vegetables. The relationship to SSP1 is in terms of reduction of food wastage leading to an improvement in other areas of environmental sustainability. Conrad et al (2018), describe in their research that an average American wasted approximately 1 pound of food every day. Thus, the period between 2010-2014 constituted an average of 30 million acres of cropland wastage. It asserts that a high-quality diet leads to more food wastage, less cropland use, and a greater waste of irrigation water and pesticides (Conrad et al, 2018). However, the food is wasted in this diet consists of fruits and vegetables which can be sustainably disposed of.
Dietary intake has a direct correlation to food waste. The choice of a healthy diet comprising of fruits and vegetables could lead to a reduction in the amount of food wastage due to sustainable forms of disposal. The ability to have healthy diets requires consumers to be economically empowered and to have a pre-plan of food items to be purchased on time. However, if fruits and vegetables are not consumed, they constitute an environmental waste. Due to the natural aspect of healthy diets, they lack the pre-waste phase that is available for most of the processed foods leading to the accumulation of waste in the environment. Processed food items such as dairy products upon expiry could lead to greater wastage of the resource.
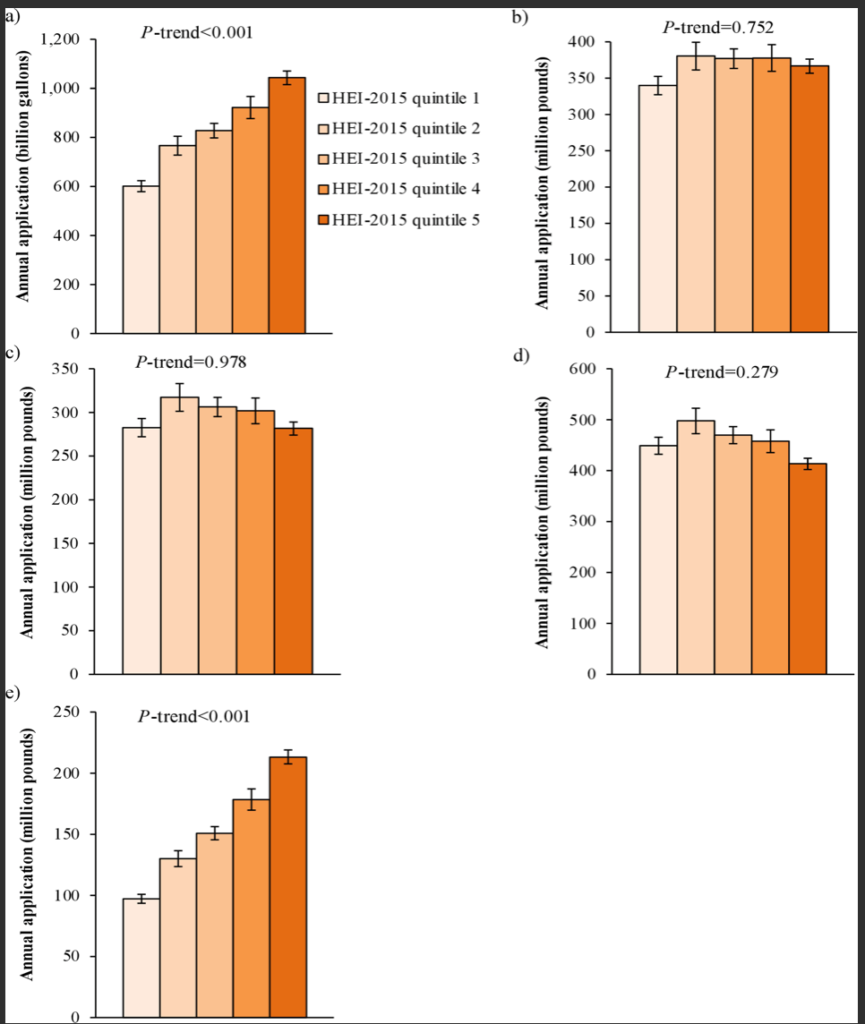
Figure 1- Annual amount of a) irrigation water, b) nitrogen fertilizer, c) phosphorus (P2O5) fertilizer, d) potash (K2O) fertilizer, and e) pesticides applied to cropland used to produce wasted food, by diet quality.
Food waste comprising of both pre-cooked food, as well as leftovers, has a major impact on the degradation of the environment. The economic and population increase is set to increase the overall food waste in the next 25 years. Paritosh et al (2017) in their research found out that in Asia about 1.4 billion hectares of land is used in the production of food that ends up being wasted. The land resources are also wasted as the product is not put to the right use. Apart from the wastage of food and water. The wasted food materials contribute to global warming due to the increase in the CO2 gas emission to the environment. The dumping of food waste in an open area could lead to more health and environmental issues.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
There is a need for proper treatment of food waste as crucial towards the achievement of the desired environmental sustainability efforts. The use of anaerobic digestion can be a useful component in the management of food waste. It helps through the production of biogas from food waste as well as recycling the food waste to generate nutrients. The article describes the anaerobic digestion constituting three elements, enzymatic hydrolysis, acid formulation, and gas production as outlined in the figure below.
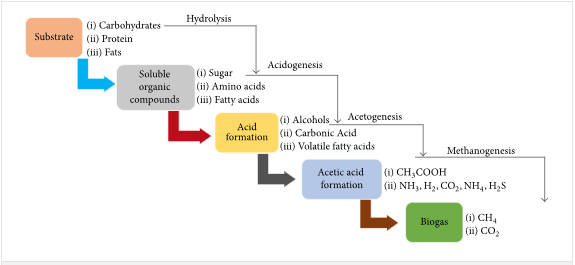
Figure 2- Anaerobic food digestion processes. The anaerobes required in the food digestion process must have the optimum conditions so as to work within the high metabolic activity.
Four Areas of Panel A
Adaptation
The adaptation measure undertaken in the reduction of food wastage is that food waste management can help animals. Pinotti et al (2020) describe the rapid growth in the world’s population as an indicator of the urgency in addressing the competition for food between human beings and animals. Sustainability efforts are important in addressing the environmental impact of the population surge and the increased demand for food. The disposal of food waste (pre-cooked and leftovers) has a huge impact on the environment with the complexities in the sustainability and profitability of the food system. Pinotti et al (2020) describe the three Rs, reduce, reuse, and recycle as being important components of the adaptation measures in food waste management in the local and the international sphere. The article, Pinotti et al(2020) focuses on the use of fruits and vegetables in the manufacture of animal feeds and helping in the reduction of food waste.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
For example, salads can be used as an alternative to the forage that is feed to the ruminants. The nutritional contents in the salad entail the minerals (potassium, calcium, and phosphorous) as well as the vitamins, A, C, and E. Salads are rich in bioactive phytochemicals and are rich in antioxidants. Additionally, the salads are easily palatable for the animals. The huge amounts of salad waste mean that the salads are continually available for making the animal feeds. This will create a need for the biomass waste to be transported from a distinct location up to the farms as part of animal feed. Extreme care will be taken so that the biomass is not contaminated, and the nutrients are not lost in the course of transportation.
Mitigation
The mitigation against the food wastage issue is that food waste can help consumers instead of becoming environmental pollutants. The dietary habits in the US and most of the westernized countries lead to a lot of wastage of processed food as well as pre-cooked food such as fruits and vegetables. Consumers need enlightenment to adapt to healthy eating habits and reduce food wastage. Conrad (2020) in his article states that the efforts to reduce food wastage help in the overall environmental sustainability efforts. American citizens on average waste one pound of food daily leading to a huge amount of environmental mass waste. The efforts to address the food wastage issue shall help in dealing with nutritional issues worldwide.
The food wastage reduction efforts can be undertaken by focusing on the amount of food that is wasted outside and within home areas. Conrad (2020) in their research found out that meat and seafood wastage normally occurs outside the home. Consumers in restaurants may purchase more food than they can consume. An effort could be consumers purchasing only the amount they can consume or restaurants serving smaller portions. On the other hand, fruit and vegetable wastage happens in home areas. Families spend much of their budget amount on items that they do not require. Adjusting the two kinds of purchases will help in the reduction of food wastage. Consumers can be enlightened on how to note whether the vegetables are just bruised, or they have spoilt. Low-income households can be educated on the need of making healthy dietary choices as a means of reducing food wastage.
Desertification
The improvement of the quality of the diet can lead to the improvement of the measures toward environmental sustainability. Conrad et al (2018) describe the widespread of the westernized diets leading to the elimination of healthy food options from the main diet. Most of the food wastage contributes to key environmental burdens such as an increased emission of greenhouse gases (GHCs). Healthy diets are often associated with lower environmental degradation as they are often associated with minimal land use, minimal use of water, and the reduced emission of greenhouse gases. Conrad et al (2018) clear the debate on whether the reduction of food wastage has an impact on environmental sustainability. The research article outlines that food waste comprises of the resources that are often used in the production of uneaten foods such as the water used, pesticides used, and the cropland where the farming took place. Reduction of food wastage will save on all the resources involved in food production thus helping in environmental sustainability.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
Williams et al (2019) describe an efficient manner in the management of greenhouse gases. Instead of green waste disposal, windrow frosting is deemed as an important component of the efficiency in the management of the number of greenhouse gases. The article, through constant monitoring of the GHC composition of the gases emitted from the windrow frosting, found out that the methane composition is lower than it is in the normal greenhouse gas emission. Thus, the article concludes that environmental sustainability shall be fostered through the adoption of windrow frosting as a means of limiting greenhouse gases.
Food Waste and Research
The persistent issues of population increase have made food waste management a critical component of the environmental sustainability efforts. The threat of the vast amount of food waste comes from the scarcity of areas for landfill and the environmental impact of the dumped food waste as well as the health risks posed by the food waste. The Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) articulates that around 1.3 billion food items get lost in the supply chain every year (Paritosh et al, 2017). The food items include waste from homes, processing industries, and the hospitality sector. In addition to the amount of food wasted, land, and additional resources such as fertilizers and water used in the processing of food items are lost. The amount of Greenhouse gas emissions due to food waste keeps on increasing with the number of food and land resource wastage. Ultimately, the number of gas emissions amount to almost 3.3 billion tons of CO2 each year.
An additional solution to food wastage is anaerobic digestion which can improve the world’s energy security. Anaerobic digestion helps in improving the production of biogas while recycling nutrients. Paritosh et al (2017) describe the anaerobic process as the generation of methane in the digestion of food waste. The process entails three main steps, enzymatic hydrolysis, acid formation, and gas production. In the first phase, the polymers are broken down throw the hydrolysis process into oligomer and monomeric units. Further on, the second phase involves the acidification of the hydrolytic products into the fatty acids. Lastly, the methanogenesis process takes place with the formation of methane gas. 30% of the methane production emanates from the CO2 reduced in the last phase of anaerobic digestion. This GHG can be used to create energy.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
Conclusion
The increasing amount of food wastage in the environment is detrimental to the efforts meant to mitigate the impacts of climate change. Poor dietary habits embodied in the overreliance on a westernized diet that is rich in carbohydrates, added sugars, beef, and processed animal products contribute to the increased food waste. Reducing food waste is conducted through educating the various users on the need of leading a healthy diet. Families are advised on budgeting for the fruits and vegetables that are important in reducing food wastage. Also, in the reduction of beef and animal product wastage, families are advised to purchase only what they can consume. Additionally, the recycling of food waste is an important measure in combatting climate change due to increased food disposal. Ultimately, environmental sustainability efforts are reliant on how much the consumers are willing to adhere to the proposed measures.
References
Conrad, Z. (2020). Daily cost of consumer food wasted, inedible, and consumed in the United States, 2001–2016. Nutrition Journal, 19(1), https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-020-00552-w
Conrad, Z., Niles, M. T., Neher, D. A., Roy, E. D., Tichenor, N. E., & Jahns, L. (2018).Relationship between food waste, diet quality, and environmental sustainability. PLOS ONE, 13(4), e0195405. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195405
Paritosh, K., Kushwaha, S. K., Yadav, M., Pareek, N., Chawade, A., & Vivekanand, V.(2017). Food Waste to Energy: An Overview of Sustainable Approaches for Food Waste Management and Nutrient Recycling. BioMed Research International, 2017, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2370927
Pinotti, L., Manoni, M., Fumagalli, F., Rovere, N., Luciano, A., Ottoboni, M., Ferrari, L., Cheli, F., & Djuragic, O. (2020). Reduce, Reuse, Recycle for Food Waste: A Second Life for Fresh-Cut Leafy Salad Crops in Animal Diets. Animals,10(6), 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10061082
Riahi, K., van Vuuren, D. P., Kriegler, E., Edmonds, J., O’Neill, B. C., Fujimori, S., … Tavoni, M. (2017). The Shared Socioeconomic Pathways and their energy, land use, and greenhouse gas emissions implications: An overview. Global Environmental Change, 42, 153–168. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.05.009
Williams, S. R., Zhu-Barker, X., Lew, S., Croze, B. J., Fallan, K. R., & Horwath, W. R. (2019).Impact of Composting Food Waste with Green Waste on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Compost Windrows. Compost Science & Utilization, 27(1), 35–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/1065657x.2018.1550023.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/

![[Solved] ENGL147N - Week 7 Assignment- Final Draft of the Argument Research Paper](https://prolifictutors.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Solved-ENGL147N-Week-7-Assignment-Final-Draft-of-the-Argument-Research-Paper--240x142.png)
![[Solution] - NR305 - Week 3 Discussion: Debriefing of the Week 2 iHuman Wellness Assignment (Graded](https://prolifictutors.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Best-Answer-NR305-Week-3-Discussion-Debriefing-of-the-Week-2-iHuman-Wellness-Assignment-Graded--240x142.png)

![[Best Answer] NR305 - Week 2 Discussion: Reflection on the Nurse’s Role in Health Assessment (Graded)](https://prolifictutors.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Best-Answer-NR305-Week-2-Discussion-Reflection-on-the-Nurses-Role-in-Health-Assessment-Graded-240x142.png)
![[Best Answer] NR305 - Week 2 Assignment: Wellness Assessment: Luciana Gonzalez (iHuman) (Graded)](https://prolifictutors.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Best-Answer-NR305-Week-2-Assignment-Wellness-Assessment-Luciana-Gonzalez-iHuman-Graded--240x142.png)

