Autonomous Trucking in the USA – A Comprehensive Analysis
June 11, 2021 2021-06-11 14:16Autonomous Trucking in the USA – A Comprehensive Analysis

Autonomous Trucking in the USA – A Comprehensive Analysis
Autonomous Trucking in USA
Introduction
Transport is an important component in urbanized areas where people have to move from one area to another either in search of goods and services or for work-related aspects. Automobiles are relied upon in the business sector as a means of moving the merchandise from manufacturing plants to the physical stores where the retailers pick them. Meldert and Boeck, (2013), states that the technological advancements in the development of autonomous vehicles are deemed as the next great revolution in automobile transport. Autonomous vehicles are going to transform the manner in which transport and mobility are perceived.
Autonomous technology is meant to transform the manner in which transportation services within the country are perceived from the first mile to the last mile of transportation. The technology changes completely the patterns in transportation while checking in the dynamics associated with the new system by making the old system obsolete. Meldert and Boeck, (2013), allude that the technological advancement in autonomous vehicle technology is evidenced by some of the licensing and legislation evidenced in private companies such as Google as well as government operations that are meant to create the technological environment for the creation of the Autonomous technology. The preparedness of various entities for the onset of Autonomous technology will be crucial in the smooth transition from the current technology to the new technology entailing automation of automobiles.
Advancement in Autonomous Tracking technology in US
Autonomous tracking technology has been advancing in India from the simplest form of technology inception to the current technology development phases. Slowick and Sharpe (2018) indicate that there are three main levels of technological advancement in autonomous tracking technology in the USA such as sensor technology, sensor technology, and software technology. Companies purchase the technological level of autonomous tracking that matches their needs and has high prospects in terms of the returns on investment. Sensor technology is the least advanced form of technological development. It brings forth the usage of Radars, Cameras, GPS, and LIDAR. Cameras are the least useful devices in the sensor technology items. They do not function optimally under certain weather conditions when it is dark, or in the event that the incoming light is too bright for the camera. Sloqick and Sharpe (2018) state that the Radar components are useful as they help in the detection of the direction of other objects emitting high-velocity waves through identification of the direction and the velocity of the objects.
Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) component is a technological available automation component that uses reflected light to detect the speed and the range of objects. It is the most reliable component of sensor technological advancement. LIDAR systems are efficient in the administration of the highways as they help in the documentation of the images captured. Sloqick and Sharpe (2018), describes the last technological component as the GPS signals. Through the use of satellite signals, the technological component helps in communication of the vehicle location and speed. Autonomous trucking can choose either of the technological components since they are readily available for purchase.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
Communications is a middle technological automation level. It relies heavily on the dedicated short range communication(DSRC) mechanisms for communicating between one vehicle and another vehicle. 5.9 GHZ band is required for successful communications within a short range distance. In USA, the technology is useful as it provides the drivers with the real time alerts from other vehicles. 5G component is a technological advancement that can help in the communication between various devices. Though the technological component is not locally available, it helps in the transmission of information from one device to another. It does not have latency as is the case with DSRC communication.
The third level of autonomous technology is software technology. Its main components are artificial intelligence and algorithms. The interconnection of the software codes enables autonomous and connected trucking. Computer software technology helps in the development of the images captured from sensor technologies interprets information from sensors or other vehicles and conveys real-time statistics. Unlike the former technological advancement levels where the only prerequisite is the purchase of the devices, software installation, and refinement to suit the need of the trucking fleet is a more complex process.
The advancement of the autonomous technology available for trucking brings in new capabilities that the vehicle can perform. Meldert and Boeck, (2013) state that various players in the industry develop the vehicles using their own specifications thus the autonomy of the vehicle can differ from another vehicle using a different kind of technology. The level of advancement in trucking will depend on the capability of the company to afford the initial cost of purchasing the device and the prospects that the technological advancement may bring to the company in terms of returns on investment. Companies taking in software autonomous technological components should be wary of the incremental costs associated with the support and maintenance of the software in use. Higher advancements in autonomous technology can be developed through the use of the advancements in the technology used and algorithms, the quality of the vehicle sensors, and the bandwidth in use.
Short Term Prospects of using Autonomous Technology
The prospects associated with the Autonomous technology are dependent on the level of automation that a vehicle has been designed in. The short term prospects of automation emanate from the vehicles that have automated the operations of the trucks at least in three levels of automation. The first prospect of autonomous technology in the short term basis is the enhancement of the security of the driver and the cargo on transit. The sensors, software and communication systems enable the vehicles to issue alerts to the drivers in case of potential harm in the course of driving. For instance, the vehicles in level 0 of automation are fitted with emergency breaks that help in breaking the vehicles to a stop while driving. Emergency breaking helps in avoiding the occurrence of many accidents in truck driving. Additional warning features such as departing from the main lane helps the driver to maintain consistency in the driving.
Sensors such as GPS configuration helps in alertness of the black spots along the route the driver is taking (Meldert and Boeck, 2013). The knowledge of the eminent black spots helps in the determination of the attitude the driver takes while driving. He is prone to be more cautious to evade the accidents that normally take place in the designated locations. Fitted Cameras helps in identification of images under visible light. Though some of the images may be blurry but the driver becomes aware of the image in the course of driving.
Autonomous trucking enables the connectivity of the vehicles as the constant communications between the connected drivers helps in visualization of the items beyond the visual scope of the driver. Vehicles along the same route help each other in information of the prevailing circumstance on the road usually captured by technological devises such as cameras. The information reduces the accidents on the road as they users get more alert on the situations on the road.
Autonomous tracking will increase efficiency in the delivery of items. Unlike human beings, machines do not need to take breaks from work or to take lunch. Thus, the time that is usually spent between the company warehouse and the retailer store is greatly reduced. Machines are efficient as most of the transit trips are conducted as planned. With human drivers, eventualities such as the driver’s sickness or a family issue could derail the progress on delivery of the required items.
Parking in major towns will be available. Autonomous vehicles mostly present the capabilities of continuity on its journey. The breaking often associated with the manual trucking is eliminated. Consequently, the overcrowding in towns often associated with the manual trucking system. In future, since there will be less need for parking spaces within the cities, the parking spaces can be transformed into more pedestrian spaces. The movement of pedestrian along the major towns shall be swift due to the minimal amount of trucks on parking. IN their research, Bagloee et al (2016) indicated that the increase in the decongestion of the major cities could have a direct impact on land around major cities. The demand for land could come down as the need for efficient transport shall be changed with the growing dynamics of the autonomous trucking. The research indicates that the population shall advance to rural locations as the areas surrounding the metropolitan locations shall be less sparsely populated.
Urban communities are accustomed to the growing need for the delivery services. Several items are purchased on the online platforms and delivered to people at their homes. The automated trucking will lead to more clean and healthy delivery of the items to people’s homes. There is no contamination of the food products that is occasioned by the multiple persons involved in the food handling business.
The advent of the autonomous trucking will bring forth change in the dynamics surrounding the liability regulation. In traditional truck driving, most of the drivers usually take liability for the accidents caused by the vehicles under their care. Autonomous trucking poses a challenge of the liability of the incidences usually associate with the vehicle. Clarity is needed whether the sellers of the technological devices or the truck owners shall be liable for all the trucks incidences.
Autonomous trucking will bring about an advantage in reducing the cost of transport. Direct costs such as the cost of fuel shall be greatly reduced. Most of the fuel consumption in vehicles occurs due to congestion and the hours spent on the distance covered during the hours of travel. The autonomous trucking will ease congestion and reduce the number of hours covered during the travel. Additional costs incurred by the public vehicle operators such as ticketing, vehicle registration and vehicle maintenance shall additionally be eliminated due to the automation of the public vehicles services.
Long Term Prospects of using Autonomous Technology
Safety of the vehicle occupants shall be improved in the long term prospect as the autonomous trucking devices helps in identification of elements that contribute to trucking accidents. Bagloee et al (2016) states that USA 2010 accident statistics indicated that there was 32,999 deaths, 3.9 million injuries, and 24 million vehicles damaged. The statistics are indicative that the direct and indirect costs implications of accident related expenses cost much. In an interesting twist of events, NHTSA (2012) recorded a decrease in the number of car accidents a phenomenon that is directly linked with an increase in the adoption of the automation technologies in the country. IIHS(2010) describes some of the technologies that have facilitated the reduction in the number of crashes in the country includes, installation of air bags, electronic stability breaks, anti-lock brakes, head protection air side bags, and forward collision warnings. Additional research indicates that at least if one third of the car are fitted with the level 0 or level 1 automation features such as the adaptive headlights, blind spot assistance, forward warning and lane departure warning. Since most of the accidents occur due to the human error, the long term prospects of inclusion of the automation features in the trucks will enhance the safety levels and help improve consistency in safety of the road users.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
In their research, Jing et al (2020) found out that the autonomous technology capabilities would bring in great value to the time spent travelling. The autonomous technology brings in the prospects of having self-drive vehicles meaning that the users get to use their time in other useful activities such as allowing people to work while on transit. The capabilities will make more people willing to spend on the various autonomous vehicles due to the value it adds to their time. Quick travel time would make more people willing to move further away from main towns and still be productive in getting to their desired locations on time. Haboucha et al (2017) states that the time spent commuting offers a lot of value to the individual users in terms of what they can do whilst on transit.
Sen et al (2020), states that the advent of the self-driving trucks will bring in positive environmental impact through the automation of the trucks automated trucks. The emissions into the environment due to the increased trucks energy usage is prone to significantly reduce due to the automation capabilities. However, the electrification of the HDT leads to an increase in the global warming due to an increase in the emissions as compared to the traditional non-automated trucks. The contribution of the automated trucks to the global warming increase out-ways the benefits gained through the automation of the functionality of the trucks as illustrated in the table below.
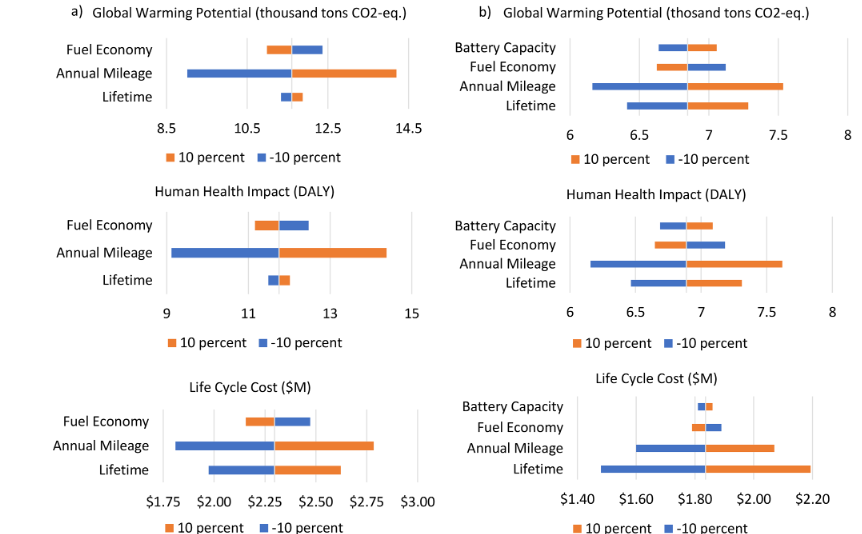
Figure 1.0 Sensitivity analysis results for (a) diesel A-HDT and (b) BE Automated-HDT
In order to solve the issue emanating from an increase in the global warming effect due to the automated functions of trucks, the Erickson 5G fully enabled Einride automated trucks could bring in the highly required solution. The 5G internet connectivity helps in providing Einride’s T-pod automated truck with the technological capabilities needed in assurance of its safety and reliability on the public roads (Erickson, 2020). 5G connectivity offers high data speeds and reduces latency on the roads through enabling optimal functionality of the fully automated trucks.

Figure 2.0 Erickson 5G enabled fully automated Einride truck
The main environmental advantage of the automated trucks is the reduction in the emissions of the CO2 gases in the environment by 90% and the minimization of the emissions of the harmful NOx and ultrafine soo particles. The automated truck provides the hope for a much sustainable future with an environmentally-friendly climate. Tsui (2020) an environmental journalist posits that electric cars could bring in the much-needed difference in environmental sustainability. He states that the air quality shall increase with an increase in electric cars since they have no emissions to the environment.
The automated truck brings in the prospects of the infrastructural changes to accommodate the changes in automated trucking. The stakeholders need to invest in the automated vehicles portable railroads as well as the docks where the trucks have ease of entry and exit. Eventually, the internet functionality needs to be fully adhered to to ensure that the automated functions in the trucks that are dependent on the trucks are still functional. The operational functions of various aspects of the government such as the ticketing of vehicles, licensing of trucks, and the standardization of the price of commodities are prone to change due to the swift mobility occasioned by the automated trucks. Cargo will have an ease of movement occasioned by the reduction of the congestion on the roads and the swiftness of movement of the automated trucks.
Early adopters of the Automated Trucks technology
The adoption of the trucking system shall not be uniform but shall vary depending on the location of the company as well as the weather in the prevailing location. Just as the technological advancement of automated trucks is sequential, its implementation shall be based on different levels of technological development. To begin with, the transition to the automation of port activities such as off-loading of cargo and transportation to locations near the port. NSF ( ) describes some of the early adopters to be fleet companies in regions with good weather such as Phoenix and Los Angeles. The desire for the early adopters to keep on running in the business is driven by the need to save money that could be spent on the driver. Also, the truck owners could save the time that could be spent on the stops done on the road. For instance, the truck proves efficiency due to the continual working hours with minimal time spent on resting or taking time off. Some of the early adopters of automated technology will be fleet operators.
Early adoption of the automated technology shall be through the pilot stages to weigh how effective a technology is in regard to improvement of service delivery. Large fleet operators are most likely to be among the initial adopters of the autonomous trucking system. The bulky installation of the technological devices on trucks shall bring in a return on investment as compared to the costs incurred. Small firms that operate on a constrained capital base will most likely fail in getting the adequate resources for the digitization of its operations. The inception of the automated technology in the market shall be comprised of equipment that shall be expensive for the normal truck operator to afford. Also, the inception phase shall be costly due to the limited capacity of the truck operators. The competition on the safety improvement technology shall be detrimental to affordability of the small firms to the new technology due to the rise in prices occasioned by increased demand.
Early adopters of the automated trucking technology shall comprise of the freight cargo operators. The cargo transporters shall incorporate the automated trucks in platooning exercise incorporating the one traditional driven truck. The platooning exercise illustrates the manner in which on truck performs the function of a lead in a fleet of automated trucks. The lead truck is interconnected with the automated trucks guiding the direction of their movement and tracking of how far the tracks are in the movement of goods and services. However, current legislation does not permit driverless cars. Platooning shall be used as a pilot study of the efficiency of the technological innovations.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
The adoption rates in the fleet company shall be variable from one fleet size to another. The fleet size operators vary from large fleet size operators, middle fleet size operators, and small fleet size operators. Dixon and Aulbur (2020) posit that small fleet operators where the driver operates as the owner of the truck company is not likely to feature among the early adopters of autonomous trucking. The small fleet operators do not have the financial capabilities of investing in the new technology which shall be expensive in its inception phase. Even though medium fleet operators may choose to invest in the new technology, they may not benefit from the operation returns that may have emanated from the costs of operation savings. Large fleets are the initial early adopters of autonomous trucking followed by the medium fleet operators. Dixon and Aulbur (2020) state that the early adopters are likely to enjoy the cost savings aspect of the new technology estimated to be at 40%.
Fleet operators are further subdivided as either commercial or private for hire. Commercial fleet operators are set to be the main early adopters of autonomous trucking technology. Mainly, the commercial fleet operators have got the capability of testing the efficiency of the new technology before it becomes fully launched in the operation of the trucks. Some of the owners of the large fleet such as the retailers, manufacturers, and logistic companies have got the capacity of checking whether an automated truck operational basis and the communication components are on check for efficiencies in its operations before rolling the autonomous trucking for the real-time operational procedures. The private fleet operators may be the subsequent adopter of the new technology after the commercial fleet operators. After the technology has been affirmed as working through the commercial fleet operators’ testing, then it can be fully implemented in the private trucks.
Time Frame for Widespread Adoption of Autonomous Trucking
The roll out of the autonomous trucking shall not be in one single defining moment; rather it shall be sequential in nature (Walker, 2019). The first kind of automation shall be based on the ability of improving the efficiency of the human drivers. Walker (2019) states that it would take a number of years for vehicles to reach the fully automation of trucks as envisioned in the level 5 of automation would take place.
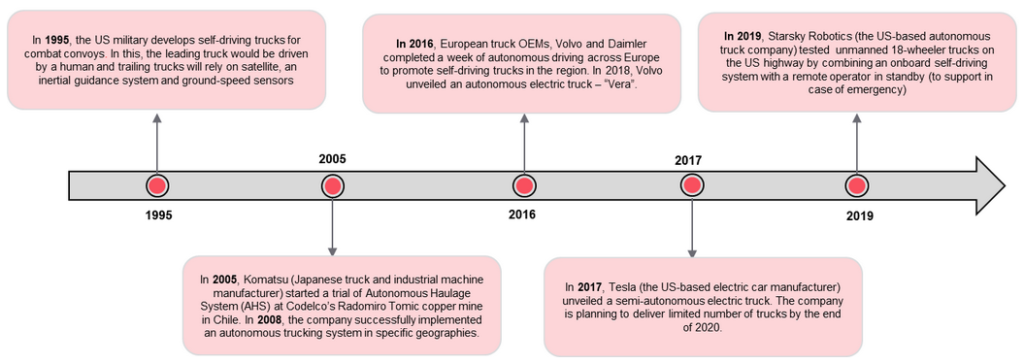
Figure 3.0 The timeline for development of the autonomous truck
The short-term goal for most companies should be the development of means in which the level four automation of vehicles can be achieved (Walker, 2019). Level four of automation depicts a state where the trucks have been technologically advanced in such a way that it does function with minimum input from the human drivers. IN a test of the efficiency of level four of operation, Otto Company, which was later bought by Uber did a test drive for a cargo containing 51,744 cans. Though the driver was present in the vehicle, he did not sit in the driver’s car and the car run on smoothly to its destination.
Future Bridge (2020) describes platooning as one of the incidences where autonomous trucking can be used as a means of experimenting with the technology involving the fuel efficiency, patient and goods safety as well as general operation ability of the new technology. In 2017 the UK government gave funds for the truck platooning trials. The trials, according to Future Bridge (2020) will comprise of the lead truck with a human driver in addition to the platooned semi-automated trucks. Essentially, the platooning was aimed at reduction in fuel consumption, reduction of emissions to the environment, and elimination of vehicle congestion in the major cities. In March 2019, the Daimler company successfully demonstrated a truck platooning (Damler, 2019). A lead truck was successfully platooned to three autonomously driving vehicles.
Regarding timelines for the adoption of autonomous trucking, the perception of the number of years required depends on the kind of industry involved such as; the startups, manufacturers, and commercial vehicles. Startups such as Otto Company estimate that the full automation of the autonomous truck is a decade away (Walker, 2019). The main idea for the startups is to have a company that will completely take over the manual operations of the driver and assures the system can maintain the movement of the trucks during the long drives. Embark, a startup company, is envisioning a transition from manual trucks to semi-automatic trucks where the drivers would take the trucks through the tricky segments of the highway (Walker, 2019). Since the state of Nevada does permit the testing of the technology, Embark Company has been testing the semi-autonomous trucking technology. The technology enables the drivers to ride on the trucks while sleeping. Embark has assigned some of the tasks to the autonomous trucks which could help in bringing the cargo to a designated location where the drivers could pick up the driving. Embark has not officially given a date where the system shall be launched for international consumption but has affirmed the system shall be ready for commercialization in the next few years.
A different kind of startup company, Starsky Robotics, envisions having a complete autonomous truck (Walker, 2019). Starsky Robotics aims at having a truck that can operate without a human driver but operating under human control. The artificial technology would steer a truck through the smooth segments of the highway, while the human control shall be useful in the rough segments of the highway. The technology will enable one driver to man more than one vehicle. Starsky Robotics is currently operating with a monitor but hopefully, the trucks would be driverless soon.
Established manufacturers like many startups envision that the full adoption of the technology shall take place in a few years to come. Daimler, one of the main players in the manufacturing of vehicles has developed the autonomous technology for both cars and trucks. Ideally, Daimler does not seek to immediately eliminate the human drivers but rather seeks to establish the technology as an aid for the driving of the trucks and cars. The new technology is seen as an optimum method of fuel saving for the trucks. Walker (2019) outlines that the Daimler company is perfecting the autonomous technology for trucks and hopefully it shall be out in a couple of years.

Figure 4.0 A self-steering Volvo truck in use on a sugar cane farm in Brazil
Volvo, has already manufactured a self-steering truck on areas that have low safety concerns as well as low speed in the manufacturing process. The trucks are tested in the sugar cane farms as illustrated above, in mines and for garbage trucks. Volvo predicts that the technology shall be available for commercialization in the next few years (Walker, 2019).
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
Commercial adoption of autonomous trucks is meant to be swifter than the manufacturers and the start-ups are suggesting. International Transport Forum concluded in their forum that within the next ten years (2030), the autonomous trucks shall be already in use on most of our roads. However, the full adoption of autonomous trucks shall depend on the manner in which the government regulations on automation of the trucks shall be developed. Government regulations would slow down the overall adoption time depending on the speed of the formulation of rules to govern the distinct operations. The ability of autonomous trucking to achieve level five of automation would help in the reduction of accidents that emanate from human errors while enabling fuel efficiency in the truck’s operations. The safety of autonomous trucks will enable quick adoption by commercial entities.
Job Implication of autonomous Trucking
Smith (2018), states that autonomous trucks could possibly replace the jobs of long-distance drivers within the next 25 years. Viscelli (2018) describes the automation of truck operations as detrimental in the trucking profession. However, amidst the fears of job loss is the new jobs that would be created in the automation of the operation of vehicles such as local driving and last-mile delivery of cargo.
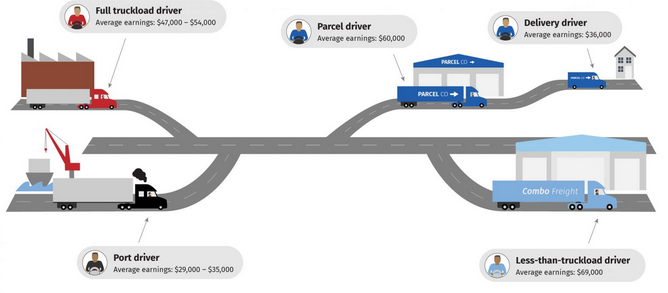
Figure 5.0 Configuration of Trucking Jobs
Viscelli (2018) describes the trucking job as one of the few jobs that do not require a college degree hence lucrative for most middle-income earners in the USA. The trucking jobs differ across various segments of the industry mainly grouped as long-distance truck drivers and short-distance truck drivers. Long-distance drivers are involved in the movement of goods from factories to distribution centers such as retail stores. Often, the long-distance drivers transport cargo for one client while on rare occasions they transport goods for more than one customer in less than truckload description (Viscelli, 2018). The Less than truckload drivers usually get better payment and are unionized. The long-distance drivers are mainly the new entrants in the driving profession and often get low wages from the companies they are working for. Local driving jobs are poorly paid as they comprise of people running errands such as deliveries and contractual workers who get paid by the number of hours they have worked such as port drivers.
The automation of trucking will lead to the loss of long-distance trucking jobs while spurring an increase in local driving jobs and delivery services (Smith, 2018). There is a wide range of adoption scenarios that would take place after the trucking services have been automated. The first scenario, according to Viscelli (2018), describes autonomous trucking as being responsible for long-distance trucking while the local jobs will be run by humans as well as non-driving jobs. Autonomous driving will be dependent on human operators to conduct routine tasks such as conducting paperwork, fueling, coupling tractors and trailers, correspondence with clients, and the manual loading and off-loading of trucks. Therefore, human drivers will adapt to the new jobs. The autonomous trucks shall start off their job at designated ports and end up at different ports letting human drivers take over and drive the trucks to the final destination.
Viscelli (2018) points out that automation could lead to the loss of more than 83,000 long-distance trucking jobs while an additional, 294,000 associated jobs with poor working conditions are prone to be lost. The long-distance drivers do less in the driving than the movement of the parcels from one job location to another, hence making their jobs to be prone to automation. The less than truckload drivers can not totally lose their jobs as they facilitate the movement of the parcels from one location to another as well as sending the parcels to the designated customers. The less than truckload drivers are some of the best-paid jobs in the industry with the drivers being more experienced and older than long-distance drivers.
The third scenario for automation of the trucking jobs would be the creation of new jobs as the e-commerce records remarkable growth as well as a reduction of the freight charges( Viscelli, 2018). The new jobs will be deemed vital for the survival of the local driving jobs with poor wages unless the licensing for the new jobs does not fully take effect. Proactive public policy is required to efficiently ensure that the subcontracted individuals such as delivery drivers for private companies do not get to poor working conditions and low wages for jobs with high turnover.
The last scenario would lead to the digitization of freight matching in the industry. Traditionally, the long-distance drivers had pressure in matching the series of loads, looking for ways to reduce the distance undertaken without freight, while looking into compliance means to the legal hours for long distance driving. Drivers are likely to experience load matching problems in physical matching exercises. Viscelli (2018), states that the issue could lead up to the automation of freight matching through the development of an application that could be available in the marketplace. The pros of digitization would be in the reduction of the miles that the truck covered without freight. The reduced cost would help in saving billions in the trucking industry every year. The cons of digitization would be the reduction of the drivers’ earnings significantly which can be countered through the proactive policy formulation.
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/
In a different study, Gittleman and Monaco (2019) state that the automation of the trucks would not in any way make the truck jobs obsolete. They describe the statistics concerning job loss as an overstatement of the researchers. To prove that the truckers driving jobs are not becoming obsolete, three reasons were formulated in their article. Gittleman and Monaco (2019), states that truck drivers on some occasions do more than just driving. The truck drivers check on the condition of the trucks, providing customer service, check on logs, and secure cargo. The tasks listed are far from automation. Therefore, the truck driver shall continually be needed in the operations comprising of the movement of cargo from one destination to another location. Customer service is an additional service that truck operators provide as they engage the customers while delivering cargo (Gittleman and Monaco 2019). The truck drivers perform the tasks that are traditionally designated for the customer care representative. Additionally, Gittleman and Monaco (2019) posit that some of the automated activities such as checking deflated tires using sensors would still need human intervention.
Gittleman and Monaco (2019) state that the trucking jobs will not be rendered obsolete by automation since full automation of trucking cannot be actualized in the near future. The automation levels range from the basic level O automation up to level 5 automation of services. In levels 0 – level 3 of automation the human intervention in the driving of vehicles is required. The current automation levels are available in the industry range from level 0-level 3 meaning that truck drivers are still needed. The full level of automation ranges between level 4 and level 5, where autonomous technology is used in the reduction of labor and thus the elimination of the drivers. However, Gittleman and Monaco (2019) state that the technology would most likely affect the long-haul drivers comprising of approximately 450,000 drivers as the technology becomes sophisticated, safer, and legally acceptable.
The third reason as outlined by Gittleman and Monaco (2019) why the trucking jobs will not be obsolete is that there are fewer truck drivers in the USA unlike what many researchers term as 3 million jobs. The total employment of the heavy truck drivers could be about 1.2 million whereas the long-distance truckers could only account for about 114,000 drivers who would be affected if level four of automation in autonomous trucking is implemented. However, the technological development of the new technology in addition to the regulatory policies could derail the extent of the job loss among the individual drivers.
Conclusion
Autonomous trucking in the USA could be the solution to the huge amounts of accidents that emanate from human error. Also, the automation of trucking is beneficial in bringing about more prospects to the country such as the value created on travel time, reduction of congestion, fuel-saving, and reduction of costs such as elimination of human drivers. Autonomous trucking is being implemented in a systemic manner from the testing of the technology in safer locations such as ports. Research predicts the full automation of trucking to take a decade (2030) but could vary depending on the government regulations. Job implications for autonomous trucking would be the loss of long-distance jobs.
References
Bagloee, S. A., Tavana, M., Asadi, M., & Oliver, T.(2016). Autonomous vehicles: challenges, opportunities, and future implications for transportation policies. Journal of modern transportation,24(4), 284-303.
Future Bridge(2020). Autonomous trucks – a revolution for the logistics sector. Retrieved from Autonomous trucks – a revolution for the logistics sector
Gittleman. M and Monaco, K (2019) Automation Isn’t About to Make Truckers Obsolete. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2019/09/automation-isnt-about-to-make-truckers-obsolete
IIHS (2010) New estimates of benefits of crash avoidance features on passenger vehicles, In: report, S. (Ed.), Insurance Institute for Highway Safety, pp. 4–5
Jing, P., Xu, G., Chen, Y., Shi, Y., & Zhan, F. (2020). The Determinants behind the Acceptance of Autonomous Vehicles: A Systematic Review. Sustainability, 12(5), 1719.
NHTSA (2012) 2010 motor vehicle crashes: overview. US Department of Transportation, Washington, DC, Research Note DOT HS 811, 552
Sen, B., Kucukvar, M., Onat, N. C., & Tatari, O.(2020).Life cycle sustainability assessment of autonomous heavy‐duty trucks. Journal of Industrial Ecology, 24(1), 149-164.
Slowik, P., & Sharpe, B.(2018). Automation in the long haul: Challenges and opportunities of autonomous heavy-duty trucking in the United States. The International Council on Clean Transportation.
Smith, J. (2018) Self-Driving Technology Threatens Nearly 300,000 Trucking Jobs Report says .WSJ magazine. Retrieved from https://www.wsj.com/articles/self-driving-technology-threatens-nearly-300-000-trucking-jobs-report-says-1536053401
Van Meldert, B., & De Boeck, L.(2016). Introducing autonomous vehicles in logistics: a review from a broad perspective. FEB Research Report KBI_1618.
Viscelli, S.(2018) Driverless?Autonomous Trucks and the Future of the American Trucker. Center for Labor Research and Education, University of California,Berkeley, and Working Partnerships USA. September 2018. https://laborcenter.berkeley.edu/driverless/.
Walker. J.(2019) Self-Driving Trucks – Timelines and Developments. Retrieved from https://emerj.com/ai-adoption-timelines/self-driving-trucks-timelines/
Need a paper like this one? Order here – https://prolifictutors.com/place-order/

![[Solved] ENGL147N - Week 7 Assignment- Final Draft of the Argument Research Paper](https://prolifictutors.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Solved-ENGL147N-Week-7-Assignment-Final-Draft-of-the-Argument-Research-Paper--240x142.png)
![[Solution] - NR305 - Week 3 Discussion: Debriefing of the Week 2 iHuman Wellness Assignment (Graded](https://prolifictutors.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Best-Answer-NR305-Week-3-Discussion-Debriefing-of-the-Week-2-iHuman-Wellness-Assignment-Graded--240x142.png)

![[Best Answer] NR305 - Week 2 Discussion: Reflection on the Nurse’s Role in Health Assessment (Graded)](https://prolifictutors.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Best-Answer-NR305-Week-2-Discussion-Reflection-on-the-Nurses-Role-in-Health-Assessment-Graded-240x142.png)
![[Best Answer] NR305 - Week 2 Assignment: Wellness Assessment: Luciana Gonzalez (iHuman) (Graded)](https://prolifictutors.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Best-Answer-NR305-Week-2-Assignment-Wellness-Assessment-Luciana-Gonzalez-iHuman-Graded--240x142.png)

